Printed as a part of the ECB Financial Bulletin, Concern 5/2019.
This text discusses the crypto-asset phenomenon with a view to understanding its potential dangers and enhancing its monitoring. First, it describes the traits of the crypto-asset phenomenon, with the intention to arrive at a transparent definition of the scope of monitoring actions. Second, it identifies the first dangers of crypto-assets that warrant steady monitoring – these dangers might have an effect on the soundness and effectivity of the monetary system and the economic system – and descriptions the linkages that would trigger a threat spillover. Third, the article discusses how, and to what extent, publicly obtainable knowledge permit the recognized monitoring must be met and, by offering some examples of indicators on market developments, affords insights into chosen points, comparable to the provision and reliability of information. Lastly, it covers chosen statistical initiatives that try to beat excellent challenges.
1 Introduction
The ECB has been analysing the crypto-asset phenomenon with a view to figuring out and monitoring potential implications for financial coverage and the dangers crypto-assets could pose to the graceful functioning of market infrastructures and funds, in addition to for the soundness of the monetary system.[1] This activity begins with the event of a monitoring framework to supply the info and insights which might be vital to repeatedly gauge the extent and materiality of evolving crypto-asset dangers with a view to making sure preparedness for any adversarial situations.
For its monitoring actions, the ECB depends to an ideal extent on publicly obtainable third-party aggregated knowledge. Quite a lot of aggregated info is out there on public web sites, which might present, as an example, metrics for crypto-asset networks, estimates of market capitalisation, costs and buying and selling volumes on crypto-exchanges and the quantity of funds raised when a crypto-asset is obtainable to the general public in “preliminary coin choices” (ICOs). These sources differ with regard to the methodologies they use, the completeness of information protection and entry to the underlying uncooked info, to call however a couple of areas. Processing the underlying uncooked info (when obtainable) brings with it appreciable uncertainty about knowledge availability and high quality owing, partly, to a scarcity of regulation of some gamers alongside the crypto-asset worth chain, whose unsupervised exercise in a borderless atmosphere usually hinders entry to dependable info. Statistics and supervisory reporting mechanisms don’t usually cowl crypto-assets (e.g. the exposures of supervised establishments to those property).
Constructing a crypto-asset monitoring framework on this foundation requires warning on account of the info points, and a stepwise strategy to filling gaps. First, it is very important establish monitoring wants based mostly on an correct characterisation of crypto-assets that enables the scope to be clearly outlined. On this foundation, as soon as the related knowledge sources have been recognized, knowledge could be collected and high quality checks utilized to make sure knowledge high quality and the consistency of methodologies and definitions. Every time potential, the ECB enhances aggregated knowledge with granular breakdowns to allow the calculation of customised indicators. However, necessary gaps stay unaddressed within the present framework, comparable to knowledge on monetary establishments’ exposures. Additional work can be wanted to extract related insights from the general public networks.
This text is organised as follows. Part 2 describes the traits of the crypto-asset phenomenon, with the intention to arrive at a transparent definition of the scope of monitoring actions. Based mostly on this characterisation, Part 3 goals to establish the related crypto-asset dangers and the financial connections, “gateway” features and different channels by which these dangers could unfold to the monetary system and the broader economic system. Part 4 discusses the indications for monitoring crypto-assets, based mostly on publicly obtainable knowledge, the provision and reliability of information (together with examples based mostly on chosen indicators for monitoring market developments), knowledge gaps and ongoing statistical initiatives that try to beat excellent challenges. Lastly, the article affords quite a lot of conclusions and factors to the way in which ahead for monitoring crypto-assets.
2 Characterising components of crypto-assets
The phenomenon of crypto-assets could be outlined and analysed from completely different views, particularly their underlying expertise, their options and the financial implications that such property[2] could have. Whereas the usage of cryptography is implicit within the alternative of the time period “crypto”-asset, conventional property comparable to cash and monetary devices can be recorded via the identical expertise – usually distributed ledger expertise (DLT). Due to this fact, DLT just isn’t a consider differentiating the brand new phenomenon from different property which might be recorded digitally by way of extra conventional applied sciences. Furthermore, the issuer of any digitally recorded asset is, in precept, free to alter the expertise used for its recording. This means that the usage of DLT as a defining aspect of crypto-assets would hamper the comparability of information over time and limits its informational content material.
To make sure the consistency of its evaluation over time and throughout applied sciences, the ECB has chosen to outline crypto-assets[3] as “a brand new sort of asset recorded in digital kind and enabled by way of cryptography that isn’t and doesn’t characterize a monetary declare on, or a legal responsibility of, any identifiable entity.” The main target is subsequently on the regulatory, financial and enterprise dimension of crypto-assets as a brand new asset class, quite than on the usage of applied sciences which might be at the moment wanted for its existence however aren’t particular to it. The truth that a crypto-asset doesn’t represent a declare on any identifiable entity implies that its worth is supported solely by the expectation that different customers will likely be prepared to pay for it sooner or later, quite than by a future money circulation on which customers can kind their expectations.
The primary characterising aspect of a crypto-asset is that it isn’t a declare on both an issuer or a custodian. Nevertheless, its customers connect worth to it as a result of they consider that: i) its provide will stay restricted, and ii) market individuals will agree on who’s entitled to promote any of the models in circulation. Shortage of a crypto-asset and the likelihood to show who can dispose of every of its models permit the existence of a crypto-asset market, the place customers on the provision facet can supply their models on the market and customers on the demand facet are prepared to bid.
A trusted bookkeeper would usually assist such beliefs by preserving a central file of what number of models of an asset have been issued and who holds them at any time limit. Market individuals may attempt to promote models they don’t personal or to promote models they personal quite a lot of instances. That may be troublesome when coping with bodily items, whose counterfeiting requires particular expertise and bodily assets and may usually be vetted by consultants, who can differentiate a replica from a real asset. When an asset is in digital kind, counterfeiting is as simple and as low-cost as copying and pasting. Because of this, within the case of property in digital kind, a trusted central get together is often tasked with controlling the variety of models (notary operate) and is accountable for preserving monitor of who owns what (bookkeeping operate).
Cryptographic strategies are used to switch the trusted bookkeeper within the recording of crypto-assets, with a view to: i) ruling out any sudden improve in crypto-assets issued on a distributed ledger, and ii) getting the community of customers to agree on who owns what (additional eliminating the necessity for a trusted bookkeeper). A distributed ledger is actually a file of data – or database – that’s shared throughout a community of customers, eliminating the necessity for a central get together to take care of the validation course of. The important thing innovation introduced by DLT is the power to distribute the validation of the recording of recent property, and of their subsequent switch, amongst a set of customers who don’t essentially belief each other and will have conflicting incentives. The community of customers could be unrestricted and may permit anyone to participate in validation, with no proof of id required, as is often the case for crypto-assets. Validation requires a voting course of amongst DLT community customers, whose particular person voting energy is determined by the particular protocol used and will forestall the formation of coalitions capable of take management of the community.
Within the case of unrestricted DLT networks, that are usually used for recording crypto-assets, there isn’t any clear governance. In reality, distributed validation is often the one governance device obtainable to agree on who owns what variety of models. That hinders the usability of the crypto-asset. To the extent that the validation mechanism goals to stop a single person (or a comparatively small coalition of customers) from with the ability to modify the content material and functioning of a distributed ledger, coordinating any change is troublesome. Even when a ample variety of customers conform to replace the protocol used, different customers are free to determine whether or not to simply accept the brand new guidelines or proceed with the outdated ones. If this occurs, a “fork” will emerge, whereby two units of customers depend on completely different units of data on particular person holdings and will by no means reconcile their views.
Any asset in digital kind could be recorded via DLT, with out essentially differing from its non-DLT equivalents when it comes to financial affect and authorized nature – therefore the identical regulation might doubtlessly apply. Recording an asset on a distributed ledger doesn’t change its financial traits or the set of hooked up dangers that warrant scrutiny by regulators. Belongings that represent a declare on an identifiable entity don’t fall below the definition and evaluation of crypto-assets on this paper, whatever the expertise used for his or her bookkeeping. This paper doesn’t subsequently cowl non-public monetary property comparable to monetary devices and funds within the type of digital cash, or business financial institution cash. Neither does it cowl central financial institution cash within the type of banks’ reserves, money, or the extensively researched however but theoretical idea of a central financial institution digital foreign money.
3 Crypto-asset dangers and linkages that warrant monitoring
The monetary system could also be topic to dangers from crypto-assets to the extent that each are interconnected; spillover results may be transmitted to the true economic system. Specifically, crypto-assets could have implications for monetary stability and intervene with the functioning of funds and market infrastructures, in addition to implications for financial coverage. ECB evaluation[4] exhibits that, whereas these dangers are at the moment contained and/or manageable inside the present regulatory and oversight frameworks, hyperlinks with the regulated monetary sector could develop and improve over time and have future implications. The discharge of the Eurosystem’s duties, particularly to outline and implement financial coverage and to advertise the graceful operation of fee methods, in addition to the Eurosystem’s duties within the areas of banking supervision and monetary stability, could also be affected. Accordingly, the evaluation concludes that the ECB ought to proceed monitoring crypto-assets, elevate consciousness of their dangers and develop preparedness for any future adversarial situation. This part goals to: i) present an outline of dangers stemming from crypto-assets, and ii) establish the primary connections which will facilitate the transmission of those dangers to the monetary system and the economic system, with a view to informing and calibrating monitoring efforts.
Crypto-asset dangers primarily originate from: i) the dearth of an underlying declare, ii) their (partially) unregulated nature, and iii) the absence of a proper governance construction.
i) Since crypto-assets haven’t any underlying declare, comparable to the correct to a future money circulation or to discharge any fee obligation, they lack basic worth. This makes their valuation troublesome and topic to hypothesis. Because of this, crypto-assets could expertise excessive value actions (volatility threat), thereby exposing their holders to doubtlessly giant losses. Relying on the circumstances of a potential value crash, the consequences could also be handed on to the collectors of the holders (if the positions contain leverage) and different entities.
ii) Crypto-assets, as outlined on this article, can hardly fulfil the traits of fee and monetary devices[5] and, as such, fall exterior the scope of present regulation.[6] On condition that they’re unregulated, their holders don’t profit from the authorized safety related to regulated devices. For example, within the occasion of chapter or hacking of a crypto-asset service supplier that controls entry to prospects’ holdings of crypto-assets (e.g. custodian pockets suppliers), the holdings would neither be topic to preventive measures (e.g. safeguarding and segregation) nor profit from schemes or different preparations to cowl any losses incurred. In view of the present state of regulation, there may be restricted scope for public authorities to control crypto-assets.[7] Any such intervention could also be additional difficult by the dearth of governance and distributed structure of crypto-assets (see beneath), in addition to their cross-border dimension.
iii) As the usage of DLT permits crypto-assets to dispense with an accountable get together, the roles and duties for figuring out, mitigating and managing the dangers borne within the crypto-asset community can’t be (clearly) allotted. From this attribute derive, amongst others, heightened cash laundering and terrorist financing dangers, to the extent that there isn’t any central oversight physique accountable for monitoring and figuring out suspicious transaction patterns, nor can regulation enforcement companies goal one central location or entity (administrator) for investigative functions or asset seizure.[8] In view of the dearth of formalised governance, it could even be troublesome to deal with operational dangers, together with cyber safety dangers, and the danger of fraud. In reality, within the broader crypto-asset ecosystem, the supply of sure companies (e.g. buying and selling) is commonly centralised. In such instances, the service suppliers could be recognized and held accountable. Nevertheless, this isn’t at all times potential in decentralised fashions, which minimise or eliminate the function of intermediaries.
The extent to which the monetary system and the economic system could also be uncovered to crypto-asset dangers is determined by their interconnectedness. Specifically, i) holdings of crypto-assets, ii) funding autos, and iii) retail funds characterize the primary linkages between the crypto-asset market on the one hand and the monetary methods and the broader economic system however.
i) People and monetary establishments, together with credit score establishments/funding companies, fee establishments and e-money establishments, aren’t prohibited by EU regulation from holding or investing in crypto-assets.[9] Crypto-assets could be accessed by anybody with an web connection, without having to open an account with a crypto-asset service supplier. Monetary establishments could spend money on crypto-assets and/or have interaction in buying and selling and market making actions. Credit score establishments may present credit score to purchasers to accumulate crypto-assets or loans collateralised with crypto-assets, in addition to lend to entities that take care of crypto-assets. Furthermore, monetary establishments can present different crypto-asset-related companies (e.g. custody companies) which will end in enhancing the accessibility and fostering the usage of crypto-assets, thereby incentivising crypto-asset holdings and investments. These actions could also be motivated, amongst different issues, by monetary establishments’ curiosity in purposes counting on DLT.
ii) Derivatives and funding autos join traders with the crypto-asset market with out them having to carry crypto-assets straight. Funding autos embrace exchange-traded merchandise (ETPs) and contracts for distinction (CFDs) that monitor crypto-asset costs. As well as, ICOs – a largely unregulated approach for companies to lift capital by producing new crypto-assets in a approach much like preliminary public choices – have began to lift curiosity amongst traders since 2017, motivated by excessive returns on funding. It must be famous, although, that these “cash” could range considerably when it comes to their traits and features: as an example, they might supply types of funding in an organization that could be linked to securities, or merely grant entry to (future) merchandise/companies provided by the issuer. Suffice it to say, for our functions, that these “cash” could not qualify as crypto-assets as outlined in Part 2, to the extent that they’ve an issuer.
iii) Beneath sure circumstances, crypto-assets could also be used for retail funds. Use instances vary from service provider funds, worldwide remittances and business-to-business (B2B) cross-border funds, to micro-payments and machine-to-machine (M2M) funds,[10] and could also be pushed by DLT-driven effectivity features as these segments are usually characterised by complexities and excessive prices. It must be famous that, whereas holders of crypto-assets can switch crypto-asset models with out an middleman by accessing straight the decentralised crypto-asset community, person comfort has led to the emergence of service suppliers that facilitate the usage of crypto-assets for funds, e.g. by dealing with funds on behalf of retailers that settle for crypto-assets and by decreasing their publicity to cost volatility. Usually, although, end-users nonetheless make and/or obtain funds in nationwide foreign money(ies) and aren’t required to carry crypto-asset balances, whereas the function of crypto-assets is restricted to enabling a back-end channel for the transaction, significantly in cross-border funds.[11]
New and present intermediaries present the “gateway” features that facilitate the interconnections between crypto-assets on the one hand and the economic system and monetary markets however. Inside the broader crypto-asset-related actions, gateway features describe the actions that allow the inflows and outflows of crypto-assets from the crypto-asset market to the monetary methods and the economic system, i.e. crypto-asset buying and selling and custody/storage. Different features (e.g. mining) or companies (e.g. promotion of ICOs) are out of scope, as a result of they dwell completely inside the crypto-asset ecosystem. Cost companies, in flip, depend on the gateway features to foster the usage of crypto-assets as a way of change.
Buying and selling platforms present the on-off ramps for customers to purchase and promote crypto-assets[12] in change for both fiat currencies or different crypto-assets. Buying and selling platforms could differ of their enterprise fashions and the companies they supply. Some buying and selling platforms could publish market quotes based mostly on their purchasers’ buying and selling exercise and, by doing so, facilitate value formation. Buying and selling platforms may be distinguished based mostly on whether or not or not they maintain crypto-assets on behalf of their purchasers, and execute trades on their books versus the DLT community(s). Some centralised platforms could present custody companies past what is required to execute/settle a commerce, through which case in addition they act as custodian pockets suppliers (see beneath) on a everlasting foundation.
Custodian pockets suppliers permit the storage of cryptographic keys which might be used to signal crypto-asset transactions. The involvement of a custodian pockets supplier is mostly requested by crypto-asset traders due to its comfort and on the premise that cryptographic keys will likely be stolen much less simply than from a private system. Custodian wallets could be both hosted on-line (additionally known as “sizzling wallets”, entailing the storage of keys on a tool that’s related to the web that enables the initialisation of transactions at any time) or offline (additionally known as “chilly wallets”, entailing the storage of keys with no connection to the web till the person must authorise a transaction). Sizzling wallets are weak to hacking by way of the web. Chilly wallets, however, are much less handy to make use of steadily however are protected against hackers and can be saved in units that may be bodily locked in vaults. In some instances, the custodian straight holds the crypto-asset models by way of its cryptographic key on behalf of the investor.
The dimensions and extent of the interconnections and gateways described above could have implications for the soundness of the monetary system, financial coverage and the security and effectivity of funds and market infrastructures:[13]
- Doubtlessly giant and unhedged exposures of economic establishments to crypto-assets might have monetary stability implications, all of the extra so since there may be at the moment no recognized prudential therapy for crypto-asset exposures of economic establishments. In its assertion on crypto-assets, whereas conceding that banks at the moment have very restricted direct exposures, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) units expectations for banks that purchase crypto-asset exposures or present associated companies, together with due diligence, governance and threat administration, disclosure and supervisory dialogue.[14] The European Banking Authority (EBA) additionally foresees the event of a monitoring template that competent authorities can problem to monetary establishments to establish and measure the extent and kind of crypto-asset exercise.[15]
- In an excessive situation, if euro money and digital fee devices hypothetically gave strategy to crypto-assets for retail fee transactions, there may very well be vital implications for financial coverage and financial exercise.[16] Nevertheless, given the traits of the crypto-asset phenomenon, significantly excessive value volatility, it’s troublesome to envisage crypto-assets fulfilling the function of a financial asset within the close to future. Having stated that, new developments aiming to mitigate volatility dangers (i.e. “stablecoins”) could show extra engaging or appropriate for fee use instances.
- Lastly, monetary market infrastructures (FMIs), significantly fee methods, securities settlement methods and central counterparties, carry the dangers of crypto-assets and will act as channels for the transmission of those dangers by the monetary system. First, monetary market infrastructures could also be uncovered to dangers from their individuals’ crypto-asset actions to the extent that adversarial crypto-asset market circumstances or different adversarial occasions could compromise individuals’ capability to satisfy their obligations. On this case, crypto-asset market-based shocks may very well be handed from one participant or infrastructure to a different/others. Second, monetary market infrastructures could pose dangers in the event that they clear crypto-asset-based merchandise or use crypto-assets for settlement, collateral or funding. Because it at the moment stands, European regulation successfully limits the utilization of crypto-assets as settlement property in monetary market infrastructures and units necessities for collateral or investments that crypto-assets don’t at the moment meet.[17] Furthermore, for EU central counterparties to clear crypto-asset merchandise, they would want to acquire authorisation from their nationwide authorities topic to demonstrating how threat administration necessities had been to be fulfilled within the mild of the particular traits to be addressed.
4 Present points in measuring the crypto-asset phenomenon
To correctly assess crypto-asset dangers and their potential affect on the monetary system and the economic system, it’s vital to enhance the qualitative evaluation on the linkages described (see Part 3) with quantitative info. On the one hand, the general public nature of crypto-asset DLT networks usually ensures transparency, i.e. transaction knowledge are open for the general public to see and confirm. Then again, the decentralised and (partially) unregulated nature of crypto-asset actions makes it troublesome to acquire particular knowledge (e.g. the variety of particular person customers) and to organise systematic knowledge assortment efforts. On this context, public web sites that monitor crypto-asset costs solely present a tough indication of market tendencies. Total, obtainable knowledge on crypto-assets are neither full nor totally dependable for the needs of monitoring market tendencies to the diploma of element essential to gauge their dangers. Furthermore, they solely permit the monitoring of worldwide tendencies with very restricted nation segregation. This part will focus on the present shortcomings in knowledge assortment and evaluation, offering concrete examples, and can suggest potential choices to beat main constraints.
4.1 Stepwise strategy to the monitoring framework of crypto-assets
Publicly obtainable aggregated knowledge already present some instruments for measuring crypto-asset dangers and their linkages with the regulated monetary system. These knowledge, topic to passing high quality checks and being complemented with different knowledge from business sources, supplied the idea of a crypto-asset dataset as step one within the ECB strategy to monitoring this phenomenon. Utilizing software programming interfaces (APIs)[18] and large knowledge applied sciences, it has been potential to create an automatic set of procedures for accumulating, dealing with and integrating a number of knowledge collections with a view to deriving customised indicators. The ECB collected knowledge from publicly obtainable and business knowledge suppliers contemplating obtainable documentation, protection and the provision of very granular aggregates or uncooked knowledge. The granularity of information, coupled with utilized knowledge high quality management measures, enabled the calculation of customised and methodologically constant indicators. Making ready constant indicators required the event of mappings and the harmonisation of data.[19]
Crypto-asset indicators tailor-made to this monitoring train have been grouped in 4 classes overlaying i) markets, ii) gatekeepers, iii) linkages, and iv) ICOs.
i) Market indicators cowl pricing and buying and selling info, together with derivatives markets. The monitoring device permits deciding on any crypto-asset or a bunch of crypto-assets from a pool of over 2,000 property at the moment traded and developing indicators on costs, traded volumes and market capitalisation in chosen models of fiat or crypto-assets. Moreover, it consists of indicators specializing in buying and selling vis-à-vis fiat currencies. With respect to derivatives, the indications supply an in depth overview of bitcoin futures contracts traded on the institutionalised exchanges of the Chicago Mercantile Trade (CME) and the Chicago Board Choices Trade (CBOE).
ii) The indications on gatekeepers cowl buying and selling platforms and wallets, as properly embrace some info on funds. The indications on buying and selling platforms present buying and selling volumes and pricing by chosen platform or a set of platforms grouped in accordance with their nation of incorporation, charges possibility, centralisation or decentralisation function and different elements. Moreover, indicators on arbitrage have been developed. With respect to wallets, info on the classification of wallets by sort, supported crypto-assets and safety features are collected. The fee section accommodates indicators on the quantity and places of ATMs supporting crypto-assets, that are those who allow the person to purchase and promote a selected crypto-asset in opposition to fiat currencies. Furthermore, some info on playing cards supporting crypto-assets is included. Such playing cards allow fee in fiat currencies utilizing crypto-assets as a deposit. Moreover, some indicators based mostly on on-chain transactions are supplied.
iii) An necessary class of indicators goals to cowl to the extent potential the linkages of the crypto-asset markets with the monetary methods and the true sector of the economic system. The indications from this class cowl for instance ETPs providing exposures to crypto-assets and indicators based mostly on statistics on holdings of securities[20].
iv) The ultimate half issues the indications for ICOs, i.e. quantity of funds raised and options, e.g. their authorized kind, the underlying blockchain and the nation of incorporation.
Nevertheless, there are nonetheless necessary gaps within the knowledge, significantly referring to sure interlinkages and to fee transactions, together with the usage of layered protocols (see Part 4.2). First, a serious knowledge hole exists with respect to the interlinkages with the true and monetary sectors, together with the quantity of banks’ or monetary firms’ direct holdings of crypto-assets and knowledge on lending for functions of investing in crypto-assets. One other space issues transactions with playing cards supporting crypto-assets, gross sales of retailers accepting crypto-assets and the worth of withdrawal transactions from crypto-asset ATMs. Lastly, an evaluation of the knowledge on transactions utilizing layered protocols is required to seize the precise extent of the usage of crypto-asset DLT networks for settlements. The dataset for the crypto-asset monitoring framework is, by definition, a consistently evolving product, because it has to maintain up with altering monitoring wants, reflecting fast modifications available in the market, whereas remaining proportionate to the potential dangers posed by the crypto-asset market.
As a second step within the growth of a monitoring framework for crypto-assets, it’s envisaged that main knowledge gaps must be closed. Total, step one within the knowledge processing cycle has been accomplished, paving the way in which for the following steps overlaying additional work on indicators and knowledge, which might shut the recognized knowledge gaps. Actions derived from suggestions from this knowledge processing cycle are anticipated to boost the info and analytical infrastructure. Work will proceed to additional develop the indications based mostly on the granular knowledge from buying and selling platforms, blockchains and official knowledge collections and statistics on the crypto-asset market, in line with the monitoring wants and proportionate to the potential dangers posed by this market.
4.2 Availability and reliability of information on on-chain, off-chain and layered protocol transactions
To evaluate the provision and reliability of information on crypto-assets, it is very important differentiate between “on-chain” and “off-chain” crypto-asset transactions. On-chain crypto-asset transactions are these recorded straight on a distributed ledger. Off-chain transactions are recorded both on the e-book of an establishment, as an example within the case of buying and selling platforms, or in a personal community of customers that use the distributed ledger of a crypto-asset to file the online transactions amongst individuals solely at a later stage.
On-chain transactions
Data regarding on-chain knowledge is commonly publicly obtainable, though its evaluation could be complicated. Most DLT protocols differ from the record-keeping that’s typical of economic accounts methods, the place an quantity of an asset is transferred by decreasing the sender’s account by that exact quantity and by crediting it to the receiver’s account. Crypto-assets are often transferred in a approach much like that of money transactions: when a person receives a amount of crypto-assets, these models aren’t divisible and must be despatched all collectively in a future transaction.[21] Due to this fact, a sender must specify what a part of the crypto-asset models collectively obtained in a earlier transaction must be transferred to the receiver(s) and what half ought to come again as “change”.
Figuring out the worth of a crypto-asset transaction and whether or not completely different crypto-asset wallets belong to the identical particular person (or establishment) is at the moment a troublesome activity. Nevertheless, it’s prone to grow to be much more difficult sooner or later. Change can both be allotted to the identical pockets from which the transaction originated or be routed to a different pockets managed by the sender.[22] Quite a lot of initiatives are being developed by the group of crypto-asset customers to make identification of those transactions tougher. Such initiatives embrace the potential for quite a lot of senders combining their crypto-asset transactions.[23]
On-chain knowledge recorded on the distributed ledger of a crypto-asset can seek advice from transactions in different property, that are recorded and transferred via an related layered protocol. Whereas the distributed ledger is often used to file just one “native” crypto-asset, its transactions can be utilized to file free-form textual content. Concretely, this textual content can include the affirmation that different property have been transferred utilizing a definite protocol.[24] Since a superficial evaluation of the on-chain transaction would solely disclose a negligible transaction within the native crypto-asset, one must interpret the transaction understanding the main points of the layered protocol with the intention to conclude that probably a sizeable transaction has occurred within the second asset.
Off-chain transactions
Varied methodological decisions are utilized in developing and supplying the very rudimentary info of the value and market capitalisation of a crypto-asset. Generally phrases, the aggregated value info of a crypto-asset is set, amongst different issues, by the choice of buying and selling platforms, the underlying buying and selling volumes, conventions regarding the 24-hour close-of-business time, elements to deal with low liquidity ranges, failures of buying and selling platforms, knowledge and connectivity. With out making use of any choice standards, pricing of crypto-assets could be very disperse.[25] Pricing info feeds additional into the calculation of the market capitalisation indicator, along with the crypto-asset provide info for which numerous choices exist.
Off-chain transactions are a rising phenomenon that goals to beat the constraints of distributed ledgers used for crypto-assets. In an unrestricted DLT community, the validation of recent transactions needs to be pricey to protect the integrity of the system and comparatively sluggish to permit ample time for all customers to agree on the most recent legitimate set of transactions earlier than a brand new one is validated. “Channels” have been launched as an answer for clusters of customers to settle transactions quicker amongst themselves and, as in web deferred settlement typical of some market infrastructures, solely use the unrestricted distributed ledger for the “final” settlement of web transactions.
Pricing and buying and selling info
Even when a enterprise associated to crypto-assets is roofed by regulation, as must be the case with crypto-asset buying and selling platforms, there are situations the place no accountable get together takes the function of operator. That is true of some buying and selling platforms which might be “decentralised”, since they depend on validation by DLT community customers to execute a commerce. Furthermore, trades agreed on decentralised buying and selling platforms usually contain the mutual switch of two property, that are settled as two particular person transactions that may hardly be recognized as constituting a single commerce.
One of many principal differentiating elements with respect to buying and selling actions and the ensuing pricing are the price traits of crypto buying and selling platforms. Amongst buying and selling platforms, these with zero-fee or transaction-fee mining options is perhaps problematic within the context of pricing and buying and selling quantity knowledge reliability. On zero-fee platforms, merchants are capable of commerce freely with out charges, no matter what number of trades they make, which can result in greater buying and selling volumes. Equally, buying and selling platforms with a transaction-fee mining function offset transaction charges with buying and selling platform native tokens. A reward of this nature may incentivise merchants to commerce extra to obtain tokens that provide useful choices as voting rights on the platform or a dividend. Each of those kinds can result in market manipulation of concurrently promoting and shopping for the identical asset to create deceptive and synthetic market exercise, additionally known as wash buying and selling.
Low liquidity, uncommon value spikes and erratic buying and selling behaviour within the round the clock market additionally contribute to the challenges of pricing crypto-assets. In contrast to every other market, the crypto-asset market operates 24 hours per day, with no standardised “shut of enterprise” time. Knowledge aggregators present decrease frequency knowledge, e.g. every day, consistent with their most popular time-frame conference, which can not coincide with that of different suppliers. To handle the problem of low liquidity, knowledge suppliers modify the contributions of the costs achieved on the much less liquid exchanges within the general indicator of a value of a crypto-asset. Uncommon spikes and erratic buying and selling behaviour are additionally corrected utilizing boundaries or different exclusion standards based mostly on benchmarks supported by, for instance, web site visitors indicators and knowledgeable judgement. The problem contributing to the issue in getting dependable knowledge covers additionally the dearth of normal naming conference for crypto-assets and their identifiers.
The uninterrupted provision of information by buying and selling platforms is perhaps affected by technical points associated to the substantial dangers of cyberattack, fraud and hacking.[26] In cyberattacks, comparable to denial-of-service assaults, the perpetrators search to make a machine or community useful resource unavailable to its supposed customers by disrupting the service of a number related to the web. That is usually achieved by flooding the focused machine or useful resource with requests. The hacking of person or platform accounts could result in the chapter of buying and selling platforms, particularly these with unsuitable technological infrastructures working in a legally unsure world digital atmosphere. Theft, cybercrime and different prison actions have affected an estimated 6% of the overall provide of bitcoin and don’t embrace the unreported instances of people who’ve misplaced bitcoins to hackers. With respect to the interruption of information provision, typical points that knowledge aggregators or exchanges expertise take the type of service outages, connectivity errors and unstable APIs.
Market capitalisation info
As a way to calculate market capitalisation the value of a crypto-asset needs to be complemented with info on the combination provide, which could be measured in a number of methods. Particularly, 4 principal measures of provide could be distinguished: i) circulating provide, ii) whole provide, iii) most provide, and iv) variations of inflation-adjusted provide, which take note of future provide inside a particular time horizon (often 5 years). Circulating provide is the perfect approximation of the models of a crypto-asset which might be circulating available in the market or are within the palms of most people. Complete provide is the overall variety of models of a crypto-asset in existence at a given second in time. Along with circulating provide, whole provide consists of these models which might be locked, reserved or can’t be offered on the general public markets and excludes models which have been verifiably burned. Most provide is the approximation of the utmost quantity of models that can ever exist within the lifetime of this crypto-asset and is pre-determined by the protocol used. Within the case of inflation-adjusted provide, a further provide scheduled, for instance, for the following 5 years is added to the circulating provide. Lastly, for some crypto-assets, most provide doesn’t exist, as there isn’t any restrict implied by the protocol.
Bitcoin futures and crypto-asset exchange-traded merchandise in Europe
Data supplied by dependable sources, comparable to institutionalised exchanges buying and selling bitcoin futures or ETPs, is probably not totally comparable resulting from variations within the specs of the underlying contracts or funding swimming pools. Bitcoin futures are traded on buying and selling platforms, comparable to BitMEX and BitflyerFX, in addition to on the institutionalised exchanges, i.e. CBOE and CME. Bitcoin futures on the institutionalised exchanges differ with respect to contract models, value limits, margin charges and tick sizes, thereby rendering the costs quoted by the 2 exchanges not strictly comparable.[27] Additional variations stem from completely different settlement bases and underlying cut-off instances.[28] ETPs traded on the institutionalised exchanges, as an example the SIX Swiss Trade[29] or Nasdaq Nordic[30] in Europe, supply exposures to bitcoin and Ethereum and are priced based mostly on numerous sources.[31]
Aggregated indicators on crypto-assets
All kinds of indicators goals to characterize the overall market of crypto-assets. These indicators are supplied on the web both by business[32] or non-commercial web sites, which provide crypto-asset-related info, funds investing in crypto-assets,[33] or analysis teams[34] and teachers.[35] For such indicators, an important methodological decisions embrace the protection of crypto-assets and pricing sources, index rebalancing and weighting schemes. With respect to the choice of crypto-assets, market capitalisation is the primary criterion used. Pricing sources are chosen based mostly on their liquidity, reliability and fulfilment of varied choice standards, e.g. compliance with anti-money laundering insurance policies. Weighting schemes are additionally based mostly on market capitalisation, usually making use of caps and buying and selling volumes. Rebalancing is carried out periodically, usually on a month-to-month frequency, however can be in near actual time.
Summing up, two features for future work emerge from the evaluation of points regarding measuring the crypto-asset phenomenon. The primary is to take care of the complexity and rising challenges of analysing on-chain and layered protocol transactions. With respect to off-chain transactions, given the numerous methodological choices, additional evaluation ought to deal with rising the provision and transparency of the reported knowledge and the methodologies used, harmonising and enriching metadata, and creating finest practices for indicators on crypto-assets.
4.3 Chosen measurement points with rudimentary indicators of crypto-asset market developments
Whereas one of many primary indicators of the scale of the crypto-asset market that’s usually used is the rising variety of crypto-assets created over time, solely a fraction of those crypto-assets is traded persistently. Out of the hundreds of crypto-assets created up to now, round 35% have been not too long ago traded on buying and selling platforms (see Chart 1) and 5% have been traded day by day for the reason that starting of 2018. Comparable developments can be noticed when trying on the indicator of the variety of buying and selling pairs. The variety of crypto-assets traded each day (i.e. inside 24-hour intervals) recovered from lows of round 1,300 on the flip of 2018 and 2019 to succeed in simply over 2,200 in April 2019. April 2019 numbers are comparatively near the file excessive of two,456 crypto-assets traded each day, recorded in September 2018. From a buying and selling persistency perspective, round 700 crypto-assets have been traded day by day for the reason that starting of 2019, one-third of them for the reason that starting of 2018. By way of buying and selling pairs, current numbers level to greater than 5,100 pairs traded each day, up from the three,000 pairs traded within the first quarter of 2019. Every single day for the reason that starting of 2019, 1,603 pairs have been traded, one-third of this quantity for the reason that starting of 2018.
Chart 1
Traded crypto-assets
(April 2019; hundreds)
Sources: Cryptocompare and ECB calculations.
If one other indicator, market capitalisation, is used for gauging the scale of the crypto-asset market, the scale varies by 20%, relying on whether or not the circulating provide or the utmost provide is chosen because the underlying measure. Latest market capitalisation based mostly on the circulating provide (estimated at USD 165 billion) has returned to 2017 ranges, having peaked on the finish of 2018, strongly mirroring developments within the pricing of crypto-assets as measured, for instance, by the CRIX index[36] (see Chart 2). Three-quarters of the overall market capitalisation is accounted for by 5 crypto-assets, which additionally make up half of the overall circulating provide of crypto-assets (see Chart 3). Market capitalisation of bitcoin alone constitutes 50% of the overall, whereas its whole circulating provide quantities to barely lower than one-third of the overall for crypto-assets. Costs of those 5 crypto-assets strongly formed the final pricing tendencies of the overall crypto-asset markets. Utilizing the utmost provide of crypto-assets to calculate the market capitalisation would imply a 20% improve within the indicator worth, with half of this attributed to bitcoin. In step with the bitcoin protocol, the utmost provide of bitcoin could be reached in 2140.
Chart 2
Market capitalisation and crypto-asset value index
(April 2019)
Sources: Cryptocompare, CRIX, Coinmarketcap and ECB calculations.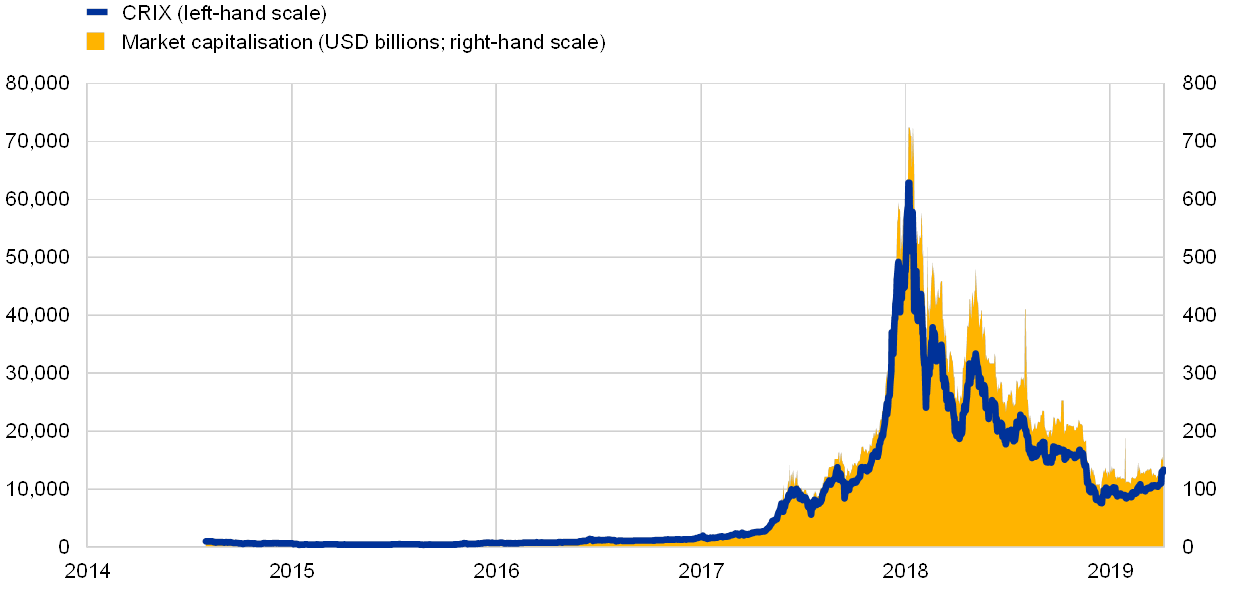
Observe: Market capitalisation relies on the circulating provide.
Chart 3
Costs, market capitalisation and circulating provide of chosen crypto-assets
(April 2019; USD)
Sources: Cryptocompare, Coinmarketcap and ECB calculations.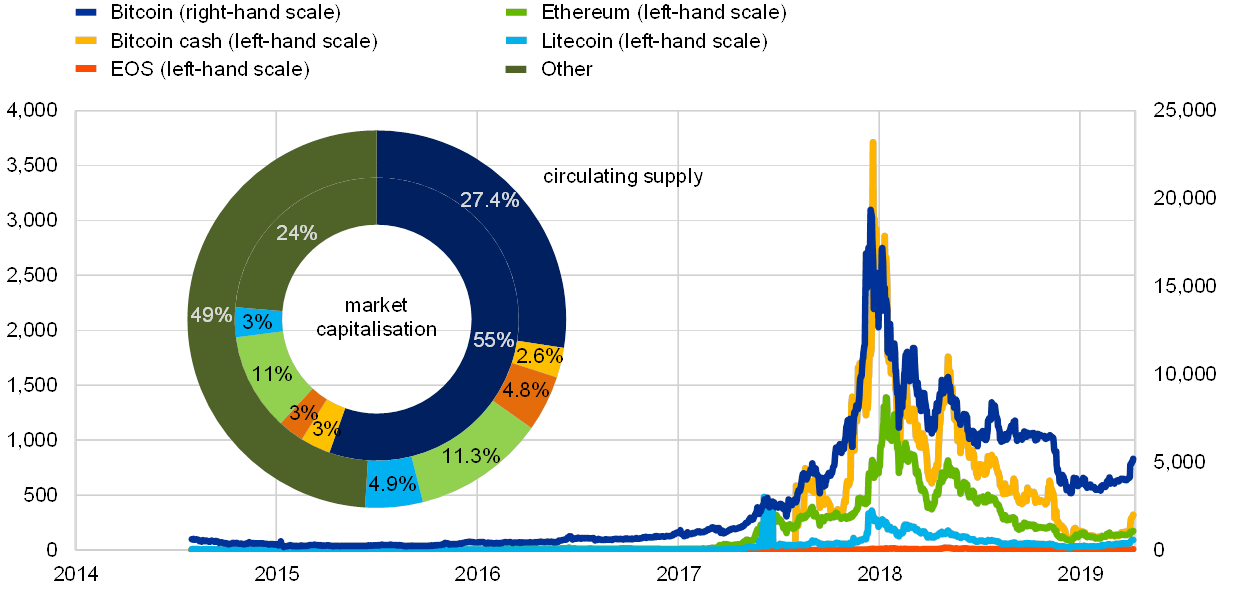
The whole market pricing and market capitalisation tendencies had been strongly formed by the combination costs of every of the 5 aforementioned crypto-assets, which on a disaggregated foundation fluctuated considerably throughout buying and selling platforms. Disregarding variations within the buying and selling and transaction charges of varied platforms, in addition to transaction processing instances and potential value actions between transactions, the value heterogeneity for crypto-assets is important (see Chart 4). The normalised interquartile ranges of the costs of 5 main crypto-assets traded versus the US greenback picked up in April 2019, though they didn’t attain end-2018 ranges of round 5% and 9% (the latter for bitcoin money). The dispersion of the costs of every of those crypto-assets throughout buying and selling platforms have decreased in 2019, in contrast with 2018 ranges and peaks across the flip of the 12 months.
Chart 4
Value dispersion for chosen crypto-assets
(April 2019)
Sources: Cryptocompare and ECB calculations.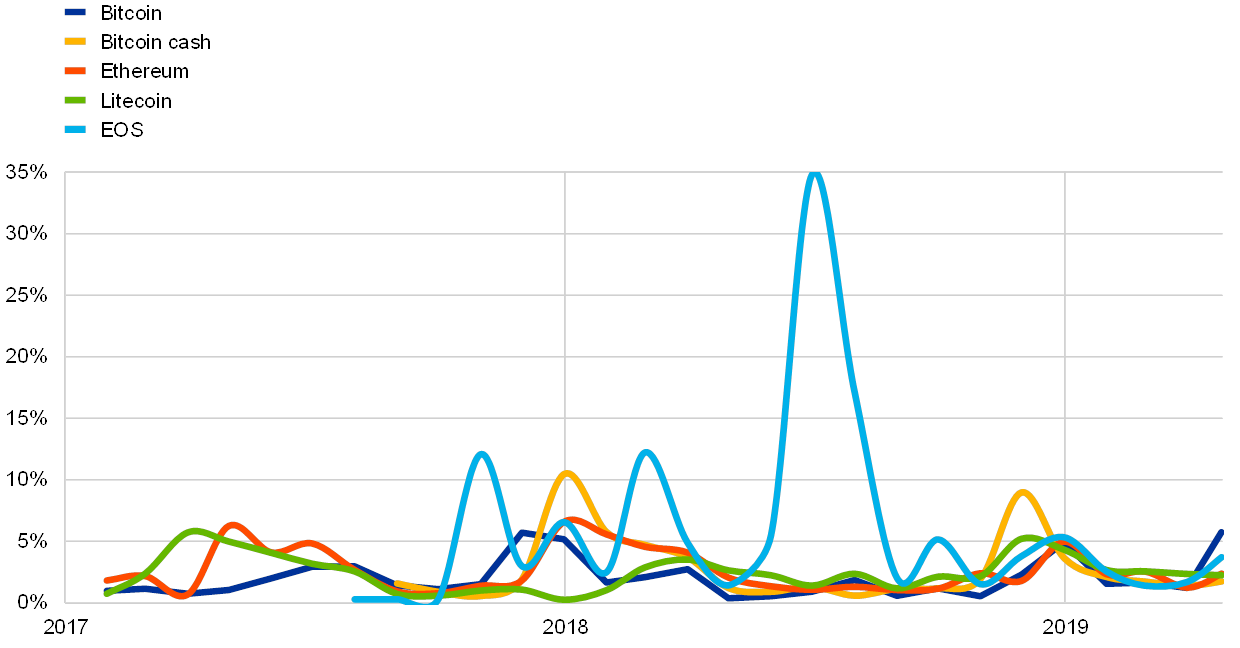
Observe: The interquartile ranges of costs of crypto-assets throughout buying and selling platforms are normalised by the typical value throughout platforms weighted by buying and selling volumes.
Buying and selling exercise vis-à-vis fiat currencies on the crypto-asset platforms has remained buoyant, albeit at decrease ranges traditionally, whereas wash buying and selling is taken into account to be vital. From the central financial institution perspective, it is very important monitor the volumes of crypto-assets which might be cleared in euro and in different fiat currencies. Trades of crypto-assets cleared in euro hovered broadly round 10% of all trades vis-à-vis fiat currencies, in contrast with an rising share of as much as 81% for the US greenback. Half of the volumes vis-à-vis fiat currencies had been recorded for bitcoin. The trades occurred, by and enormous, on centralised buying and selling platforms. Nevertheless, exercise on decentralised buying and selling platforms appears to be choosing up however nonetheless accounts for lower than 1% of buying and selling volumes. From the geographical perspective, trades on platforms positioned in Europe amounted to 24% of all buying and selling, with the best buying and selling volumes recorded on platforms in Malta and the UK, whereas trades on platforms not attributed to a rustic accounted for 30% of buying and selling volumes. With respect to scrub buying and selling, some analyses[37] level to the very excessive variety of trades affected by this market manipulation.
Chart 5
Buying and selling volumes vis-à-vis USD, euro and different fiat currencies
(April 2019)
Sources: Cryptocompare and ECB calculations.
On institutionalised exchanges, buying and selling exercise of bitcoin futures and ETPs with underlying crypto-assets peaked in April 2019; nevertheless, CBOE suspended buying and selling of bitcoin futures, whereas buying and selling exercise of ETPs on the SIX Swiss Trade is anaemic. The bitcoin futures market has declined barely for the reason that finish of 2018. Buying and selling volumes peaked strongly, although, on the CME change in April 2019, following the CBOE announcement of the suspension of the upcoming future contracts, citing enhancements within the strategy in direction of crypto-currency derivatives as a cause (see Chart 6). Turning to buying and selling exercise for ETPs on European exchanges, as measured by the variety of trades, whereas exercise is buoyant on the Nasdaq Nordic, reaching greater than 17,000 trades in April, buying and selling on the SIX Swiss Trade is weak (see Chart 7).
Chart 6
Buying and selling volumes and open curiosity of bitcoin futures
(April 2019)
Sources: Bloomberg and ECB calculations.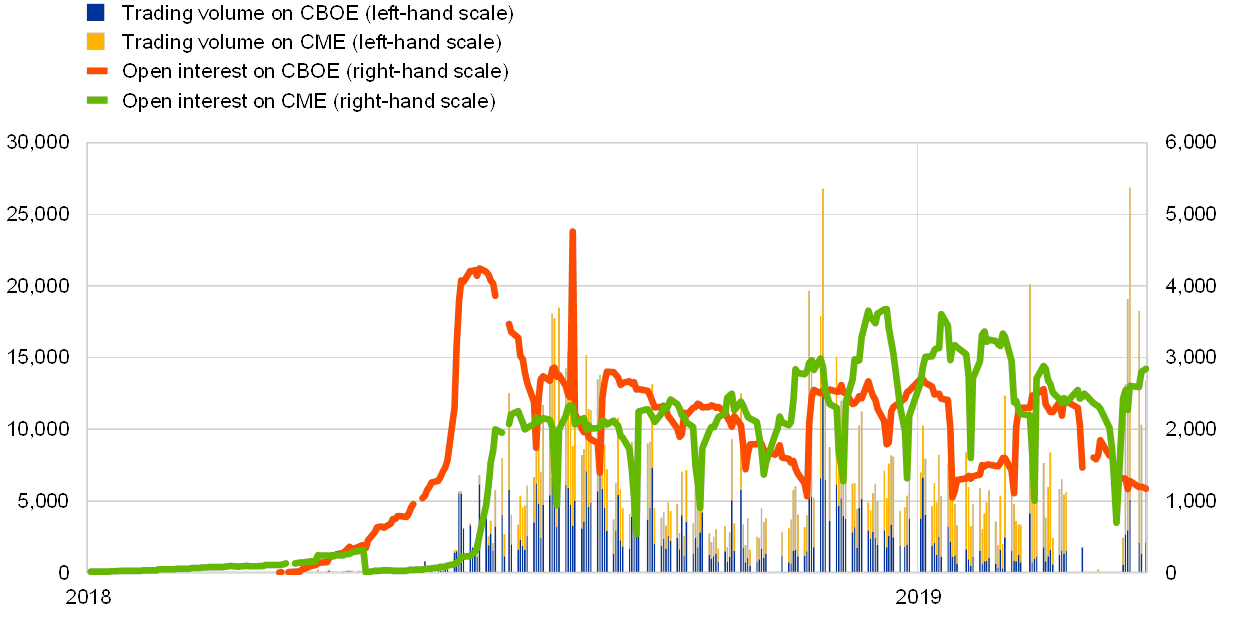
Observe: Buying and selling volumes and open curiosity seek advice from the present contracts for the forthcoming month.
Chart 7
Trades of ETPs on the European institutionalised exchanges
(April 2019; variety of trades)
Sources: Bloomberg and ECB calculations.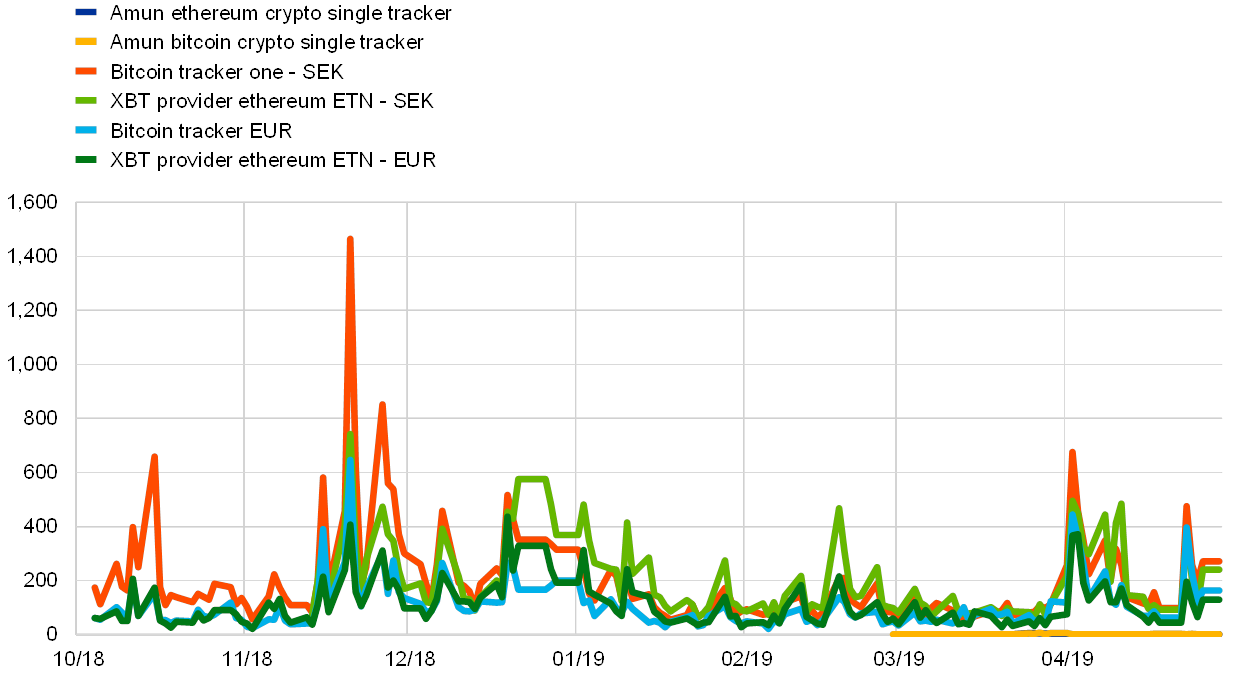
Whereas no arduous knowledge can be found for buy transactions of products or companies with settlement in crypto-assets, some indicators on the utilization of crypto-assets level to exercise choosing up barely. That is mirrored within the rising variety of ATMs supporting crypto-assets, a rise within the choices of playing cards with crypto-asset options, new wallets with expanded protection of crypto-assets and a rising curiosity by retailers in accepting crypto-assets. The variety of ATMs supporting crypto-assets is rising, with the most important numbers in the USA and Canada (2,643 and 625 respectively). The variety of comparable ATMs in Europe is approaching 1,000, which constitutes a 20% share of those ATMs worldwide, the largest presence being in the UK and Spain. With respect to playing cards supporting crypto-assets, there are a couple of new choices of playing cards in Europe that may be loaded with main crypto-assets, e.g. bitcoin, Ethereum or litecoin. Relating to wallets, the bulk are concentrating on the most important crypto-assets and have gotten extra multi-asset-oriented, with some supporting near 100 crypto-assets. For almost all of wallets, customers management their non-public keys versus the much less standard choices of storing non-public keys with a 3rd get together. Regardless of the reportedly rising curiosity of retailers in accepting crypto-assets as a type of fee,[38] no arduous knowledge on underlying transactions can be found. Nevertheless, buy transactions of products or companies with settlement in crypto-assets in Europe are estimated to be insignificant.
The variety of on-chain transactions for main crypto-assets is rising, however it solely provides a partial view of whole crypto-asset transactions as off-chain transactions aren’t taken under consideration. The variety of transactions per day on the bitcoin blockchain exhibits a gradual improve since spring 2018. Transactions on the Ethereum blockchain are at the moment on the 0.5 million degree, after peaking in January 2018 at 1.3 million per day. Transactions on the bitcoin money blockchain not too long ago confirmed an upward development, from 4,000 to 38,000 transactions per day. This adopted a couple of excessive spikes in winter 2018 after the cut up of this crypto-asset. Lastly, transactions on the litecoin blockchain remained quite secure at round 25,000 transactions per day. Evaluating the values of the transactions recorded on these blockchains with the buying and selling values on buying and selling platforms, the on-chain transactions account for a small fraction of the worth of off-chain transactions (see Chart 8).
Chart 8
On-chain transactions for chosen crypto-assets
(April 2019; left panel: hundreds of thousands/day; proper panel: percentages)
Sources: Bitinfocharts, Cryptocompare and ECB calculations.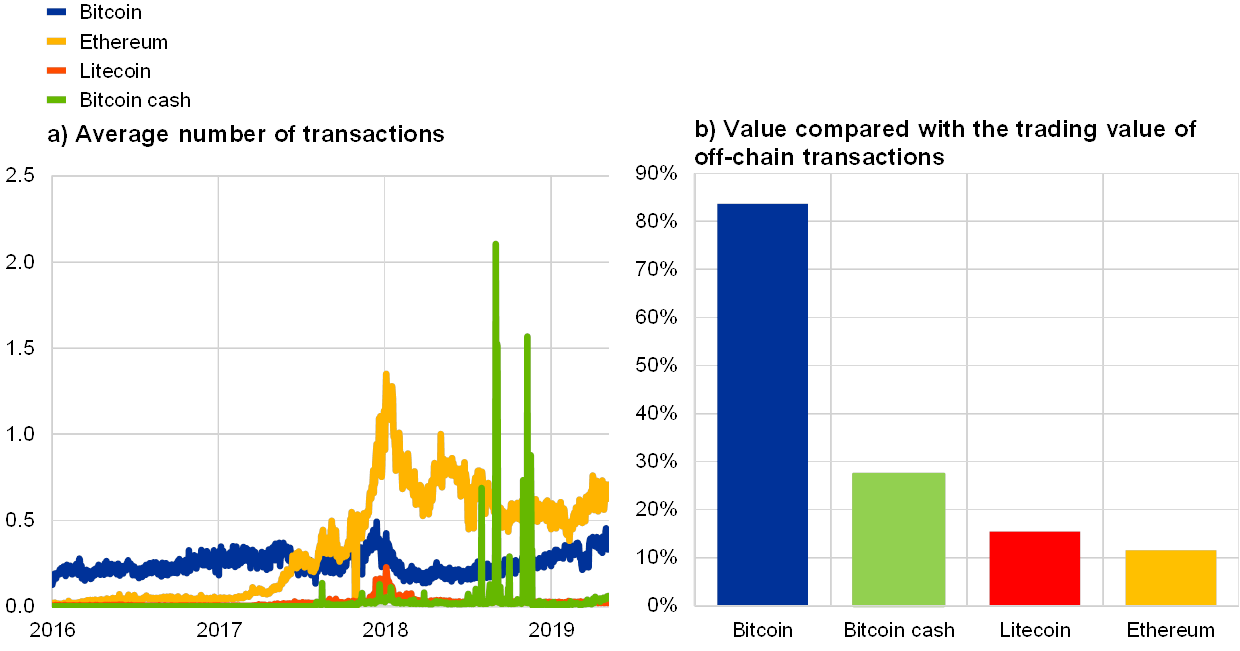
Total, chosen indicators present that the crypto-asset market is resilient, however evaluation must be interpreted with warning on account of uncertainties associated particularly to vital value dispersion, wash buying and selling and the unavailability of arduous transaction knowledge. Regardless of the broad decline within the off-chain costs of crypto-assets, following a peak on the finish of 2018, within the crypto-asset market a excessive variety of crypto-assets proceed to be traded day by day on the buying and selling platforms and exercise is secure on some institutionalised exchanges. This evaluation can be supported by the rising values of on-chain and off-chain transactions per day for main crypto-assets. Then again, value dispersion of crypto-assets throughout buying and selling platforms is substantial, pushed to some extent by wash buying and selling. Furthermore, the dearth of detailed info on crypto-asset transactions hinders evaluation.
4.4 Statistical initiatives to enhance info on crypto-assets
Statistical points associated to crypto-assets, additionally inside the broader matter of fintech, have been adopted by the central financial institution group, for instance the Irving Fisher Committee (IFC) on Central Banking Statistics.[39] Particularly, the IFC has arrange a working group on fintech knowledge points[40] whose goal is to analyse and make potential suggestions for central financial institution statistics. The purpose of the IFC’s work is twofold. First, it’s to take inventory of present knowledge sources and assess central banks’ further info wants, which must be addressed by the IFC survey of the member central banks. Second, it’s to analyze key knowledge gaps, along with the prices and advantages of initiatives to deal with them, and supply steerage for creating ample statistical definitions.
Moreover, the statistics group[41] has began to analyze the statistical classification of crypto-assets within the System of Nationwide Accounts (SNA), which can have vital implications on the measurement of GDP and different key indictors and supply additional perception into crypto-asset-related actions. Nationwide accounts are a knowledge supply for numerous financial indicators, comparable to GDP and its parts and derived indicators, which offer perception, for instance, into the scale of the economic system and the primary drivers of financial exercise. The statistical classification of crypto-assets and associated exercise within the SNA could considerably affect key indicators, together with the GDP for some nations, relying on the tactic chosen.[42] Complexity within the statistical classification of crypto-assets derives from the very attribute of crypto-assets not representing a monetary declare on, or a legal responsibility of, any identifiable entity. Growing harmonised statistical therapy of crypto-assets consistent with the final nationwide accounts steerage for earnings, worth technology, asset creation and accumulation would supply additional perception and assist to deal with present knowledge and analytical challenges.
Inside the European System of Central Banks (ESCB), the ECB has established an off-the-cuff community on crypto-asset knowledge to analyse choices to boost info on crypto-assets. Following on from the preliminary inside work on the ECB, an off-the-cuff community of representatives from the ESCB was created to analyse the choices for addressing recognized crypto-asset knowledge gaps. The work of the community focuses on the advance of the prevailing knowledge and indicators, investigation into new sources for evaluation and nearer collaboration on analytical work overlaying statistical points. Within the medium time period, the community plans to replicate additionally on the problems associated to the classification of crypto-assets in central financial institution statistics.
Statistical initiatives involving central banks can present useful contributions to closing the recognized crypto-asset knowledge gaps sooner or later. There was no complete world initiative for creating and compiling statistics on crypto-assets in a structured approach earlier than. Sooner or later, central banks can present enter with respect to the brand new knowledge sources for info on the interlinkages of crypto-assets. Drawing from the obtainable instruments, central banks might contribute to closing knowledge gaps by way of initiatives in direction of elevated availability and transparency of information, indicators and methodologies, finest practices, in addition to potential statistical compilations.
5 Conclusions
Crypto-assets are enabled by DLT and characterised by the dearth of an underlying declare. Within the mild of the implications they could have for the soundness and effectivity of the monetary system and the economic system, and likewise for the fulfilment of the Eurosystem’s features, crypto-assets warrant steady monitoring. To this finish, the ECB has arrange a dataset based mostly on high-quality publicly obtainable aggregated knowledge complemented with different knowledge from some business sources utilizing API and large knowledge applied sciences. Nevertheless, necessary gaps and challenges stay: exposures of economic establishments to crypto-assets, interlinkages with the regulated monetary sectors and fee transactions that embrace the usage of layered protocols are all examples of domains with outstanding knowledge gaps.
The challenges in measuring the phenomenon of crypto-assets are various and relate each to on-chain and off-chain knowledge. Particularly, it’s arduous to retrieve public knowledge on segments of the crypto-asset market that stay off the radar of public authorities; some comparatively illiquid buying and selling platforms could also be affected by wash buying and selling; and there’s no consistency within the methodology and conventions utilized by institutionalised exchanges and business knowledge suppliers. Furthermore, new and sudden knowledge wants could properly come up with additional developments in crypto-assets and associated innovation.
Statistical initiatives by the ECB and the central banking group are anticipated to supply a useful enter to efforts geared toward closing the info gaps related to crypto-assets. Wanting forward, the ECB will proceed to work on indicators and knowledge by coping with the complexity and rising challenges encountered in analysing on-chain and layered protocol transactions. Moreover, investigation will proceed relating to the brand new knowledge sources for info on interlinkages of crypto-assets. With respect to the off-chain transactions, amid a mess of methodological choices, additional work will deal with rising the provision and transparency of the reported knowledge and the methodologies used, harmonising and enriching the metadata and creating finest practices for indicators on crypto-assets.
